Therapies
Psychotherapies for schizophrenia include cognitive behavioural therapy, family therapy, case management, psychoeducation, and group therapy. There are a range of other options such as art and drama, dance and music therapies, as well as animal-assisted therapy and mindfulness, among others. Click on the tabs below to access all the information, or browse via the drop-down menu on the left.
Image: ©freshidea – stock.adobe.com

Acceptance and commitment therapy
We have not found any systematic reviews on this topic that meet our inclusion criteria. Pending enough primary studies, we invite reviews on this topic to be conducted. Alternatively, we will endeavour to conduct our own review to fill this gap in the Library. September 2020

Animal-assisted therapy
What is animal-assisted therapy? Animal-assisted interventions use trained animals to help improve physical, mental and social functions in people with schizophrenia. It is a goal-directed intervention in which an animal that meets specific criteria is an integral part of the treatment process, which usually involves pharmaceutical and psychosocial treatment components. It has been shown to improve outcomes for people with autism-spectrum symptoms, medical difficulties, and behavioural problems. What is the evidence for animal-assisted therapy? Moderate to low quality evidence suggests animal-assisted therapy may improve social functioning, symptoms, treatment adherence, self-esteem, and self-determination. September 2020

Art and drama therapies
What are art and drama therapies? Art therapy is defined by the British Association of Art Therapists as “the use of art materials for self-expression and reflection in the presence of a trained art therapist. Clients who are referred to art therapy need not have previous experience or skill in art, the art therapist is not primarily concerned with making an aesthetic or diagnostic assessment of the client’s image. The overall aim of its practitioners is to enable a client to effect change and growth on a personal level through the use of art materials in a safe and facilitating…

Case management
What is case management? Case management is a community-based program in which a nurse, social worker or other clinician oversees the treatment programs and overall wellbeing of patients. Intensive case management is a variation on standard case management, where case managers have a smaller load, generally fewer than 20 patients. It is often used to care for people at high risk of hospital readmission. Assertive community treatment is a form of intensive case management with a focus on service coordination involving extensive integration with multidisciplinary teams who share a small caseload. What is the evidence for case management? Compared to…
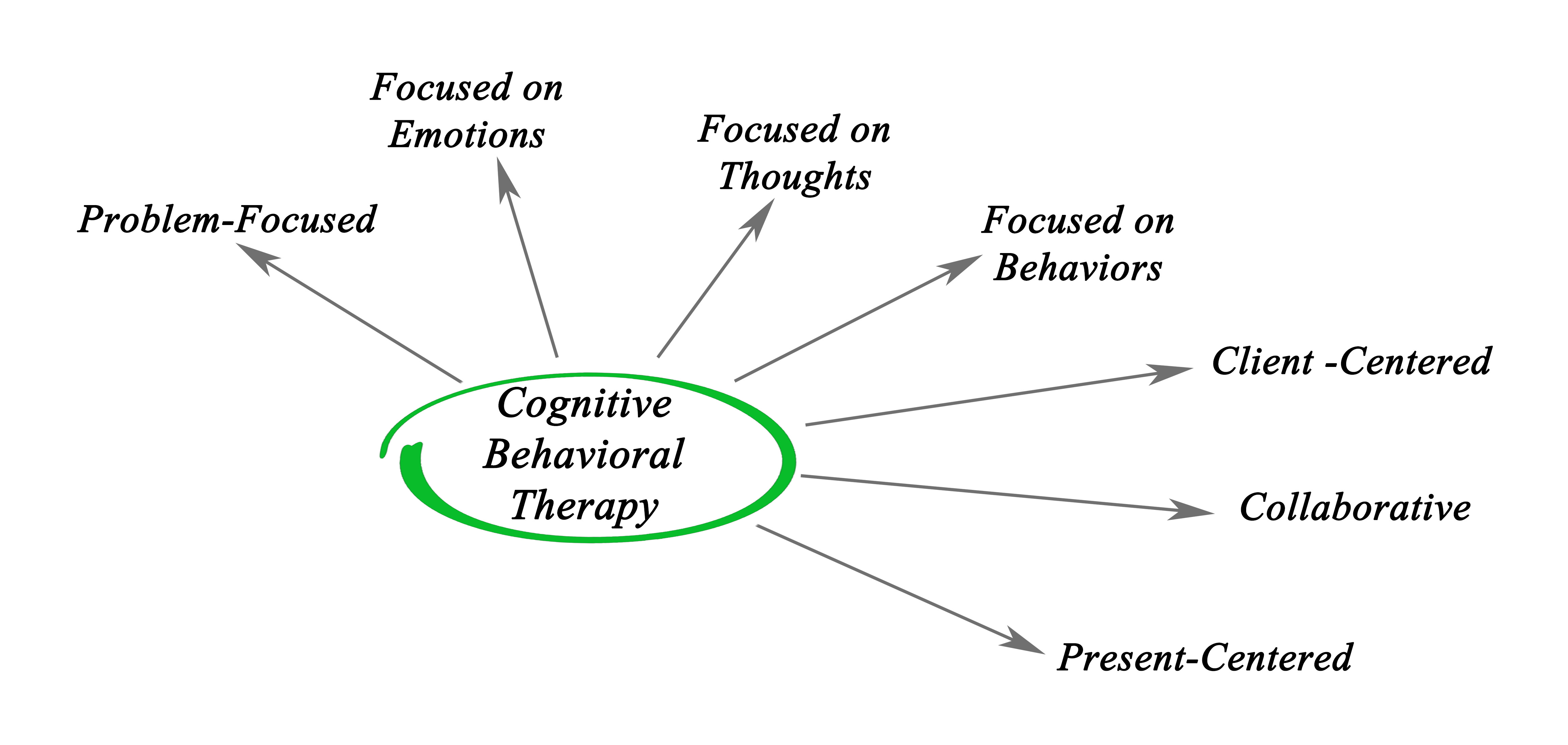
Cognitive behavioural therapy
What is cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT)? CBT aims to generate links between patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behaviours using cognitive restructuring to facilitate the understanding and management of behaviours. It can be used for improving positive or negative symptoms, as well as other factors including depression, psychotic relapse and coping. What is the evidence for CBT for people with schizophrenia? Moderate to low quality evidence shows small improvements in global state with CBT in the long-term (>1 year), but not in the short-term (<6 months). There may also be some improvements in symptoms, but no consistent benefit was found for…

Community care
What is community care? Community care refers to community-based interventions that involve medication, psychosocial treatments, monitoring of clinical progress, and housing and supportive services. These programs encourage patients to establish meaningful relationships, occupations and activities, while also establishing routines at home. Community treatment may also involve involuntary outpatient commitment (compulsory community treatment) to ensure patients receive their necessary treatment. What is the evidence for community care for people with schizophrenia? Moderate to low quality evidence suggests community care provides some benefit for medication adherence. There were no differences between compulsory and voluntary community care in the number of hospital readmissions, the number of hospital bed…

Cost
What are treatment costs? The burden of schizophrenia includes direct costs, indirect costs, and intangible costs. Direct costs are estimated by the amount of services used and the price of treatment. Indirect costs are estimated by the averaged reduced future earnings of both patients and caregivers. Intangible costs are those that may be associated with the illness, such as trauma and depression. This topic presents the current evidence on the direct costs of psychosocial treatments. What is the evidence for the costs of psychosocial treatments? Low quality evidence is unclear as to the cost effectiveness of psychosocial treatments. Review authors…

Crisis intervention
What are crisis interventions? People with severe mental illnesses such as schizophrenia may be in need of emergency care at some stage in their illness, particularly in the early stages. Crisis intervention is a treatment model designed to offer intensive crisis-focused treatment to people living in the community, and is usually provided in the context of home-based care. Crisis intervention programs comprise teams of specialist staff who often provide 24-hour availability of support. This may be a mobile treatment, a dedicated unit based in a hospital or day centre, or a residential. What is the evidence for crisis interventions? Moderate…

Crisis planning
What is crisis planning? Crisis planning involves people planning for their care in the event of a future mental health crisis. Types of crisis planning vary, however, they all strive to incorporate a person’s preferences for the care they would like to receive, as well as care they want to refuse, during a crisis. Joint plans are developed collaboratively between the patient and mental health professionals. Crisis planning may help prevent relapse by promoting better self-management. They may reduce the need for hospital admissions by encouraging prompt help-seeking or improved community service responses. They may also encourage patients to accept…

Dance therapy
What is dance therapy? Dance therapy refers to the use of physical movement is a therapeutic context, aiding the expression of emotions and experiences. The American Dance Therapy Association defines dance therapy as the “psychotherapeutic use of movement for furthering emotional, social, cognitive and physical integration of the individual.” Dance therapy does not entail any specific or choreographed therapeutic ‘dance’; instead, the therapeutic nature of dance is completely individualised, and guided by a therapist based on an individual’s needs. What is the evidence for dance therapy? Moderate to low quality evidence suggests dance therapy may have a small benefit for…

Day centres and day hospitals
What are day centres? Day treatment programs and day hospitals are medically focused community-based units, often described as an intermediary between inpatient and outpatient hospital care. This type of program provides a more engaged, integrated treatment service than traditional outpatient units and incorporate diagnostic, medical/psychiatric, psychosocial, and prevocational treatment services. What is the evidence for day centre programs? Moderate to low quality evidence suggests there may be a longer duration of treatment in day hospitals compared to inpatient care. There appears to be no benefit of day hospitals over outpatient care for reducing hospital readmissions. Low quality evidence is unable…

Dialectical behavioural therapy
We have not found any systematic reviews on this topic that meet our inclusion criteria. Pending enough primary studies, we invite reviews on this topic to be conducted. Alternatively, we will endeavour to conduct our own review to fill this gap in the Library. September 2020

Distraction techniques
What are distraction techniques? Distraction techniques are a form of coping skill, taught during cognitive behavioural therapy. These techniques are used to distract and draw attention away from the auditory symptoms of schizophrenia, such as auditory hallucinations (e.g. voice-hearing) and intrusive thoughts. These approaches are not a stand-alone intervention for schizophrenia, but rather a strategy for coping with illness symptoms, used in conjunction with ongoing pharmaceutical and psychological therapies. There are three key ‘distraction’ approaches: cognitive distraction, behavioural distraction, and physiological distraction, though techniques can overlap. Cognitive distracters can include reading aloud, humming, as well as voice mastery (e.g. replying…

Educational therapies
What are educational therapies? Educational therapies for psychiatric illnesses (psychoeducation) are targeted towards increasing a person’s knowledge about their disorder. Educational therapies aim to improve insight and understanding, promote coping and reduce stigma, increase medication adherence, enable behavioural change, and ultimately prevent relapse. Educational sessions can take place individually or in groups with other patients or with family, and are usually incorporated into an ongoing treatment regimen. What is the evidence for educational therapies? Moderate to high quality evidence suggests psychoeducation in general has a medium-sized benefit for reducing relapse and rehospitalisation rates, and for improving treatment adherence. It also…
Enriched intervention
What is enriched intervention? Enriched interventions are comprehensive treatment paradigms that are specialised for particular illness phases, or extensively tailored to a patient’s individual needs. Such intervention programs for schizophrenia and psychosis are often combined interventions comprising pharmaceutical and psychosocial therapies. Enriched interventions are often applied as early intervention programs in first episode psychosis or schizophrenia. What is the evidence for enriched intervention? Moderate to low quality evidence suggests enriched interventions are more effective than standard care for improving symptom severity, but not for improving functioning. September 2020

Family intervention
What is family intervention? Family intervention includes family members in therapeutic sessions with the goal of improving all family members’ mental health and understanding of the disorder. This type of intervention aims to enhance the capacity of both patients and their families for problem solving and illness management. Family interventions have a focus on providing information about the disorder, and emphasizing instructions for medication and treatment adherence. Therapeutic sessions can also involve cognitive behavioural interventions to improve problem solving and communication skills and to reduce high familial expressed emotion. What is the evidence for family intervention? High quality evidence finds…

Genetics counselling
We have not found any systematic reviews on this topic that meet our inclusion criteria. Pending enough primary studies, we invite reviews on this topic to be conducted. Alternatively, we will endeavour to conduct our own review to fill this gap in the Library. September 2020

Group therapy
What is group therapy? Group therapy refers to any psychosocial therapy that is administered in a group setting. It can include specific cognitive or behavioural therapies. It is often utilised in inpatient settings. The usefulness of group therapy has been examined in the context of improving illness outcomes such as symptom severity and quality of life, medication compliance and particularly social interaction and anxiety. What is the evidence for group therapy? Moderate to high quality evidence suggests a small effect of improved overall patient outcomes with group psychotherapy over various control conditions. September 2020

Home-based care
What is home-based care? For people with schizophrenia, there are many options for receiving treatment. For patients in chronic or stable phases of the illness, some interventions and treatments can be provided in a home environment. These types of interventions are integrated as part of a comprehensive treatment program in conjunction with ongoing medication. What is the evidence for home-based care? Moderate to low quality evidence finds improved overall symptoms and social adjustment by 20 months (but not 12 months), more sociable behavior and less agitation and disorientation by 4-6 months, less family burden and disruption by 3 months (but…

Hypnosis
What is hypnosis? Hypnosis may be experienced as an altered state of consciousness or as a state of relaxation. There is no agreed framework for administering hypnosis, but the procedure often involves induction (such as eye fixation), muscular and/or breathing relaxation, guided imagery and orientation to the surroundings. Hypnosis is a controversial intervention that must be investigated with clinician input. What is the evidence for hypnosis? Moderate to low quality evidence suggests no difference in study retention between patients receiving hypnosis and control conditions. Low quality evidence is unable to determine any benefit of hypnosis for symptoms or functioning. Review…

Inpatient and outpatient care
What is inpatient and outpatient care? Treatment that is provided to patients in a home environment, community or outpatient mental health facility are more commonly provided for patients in chronic or stable phases of the disorder. Treatments are integrated as part of a comprehensive program in conjunction with ongoing medication. Patients in a more acute phase of illness are usually treated through psychiatric inpatient hospital services. What is the evidence for inpatient care and outpatient care? Moderate to low quality evidence finds improved overall symptoms and social adjustment with home-based crisis intervention by 20 months, more social behaviour, less agitation…
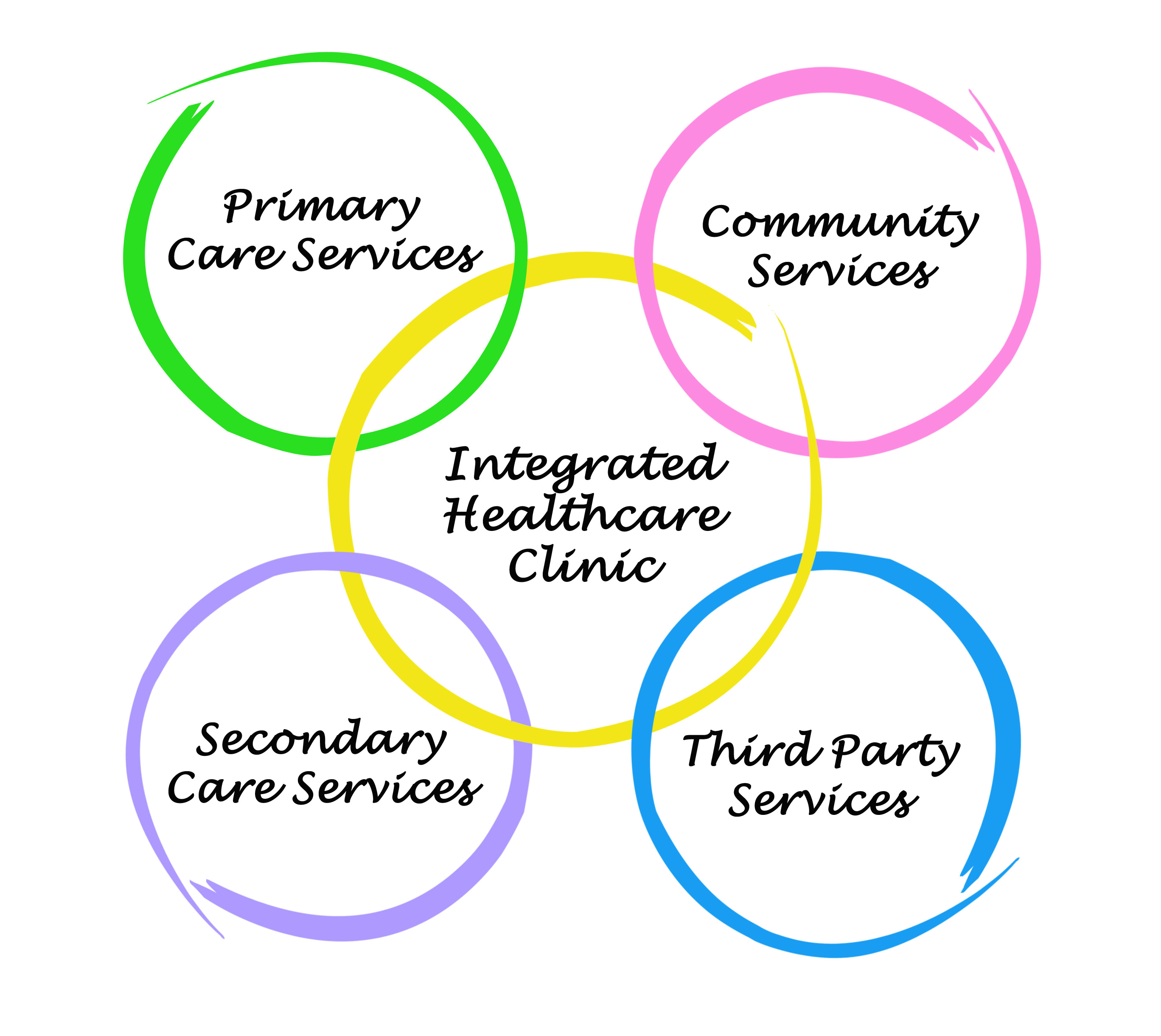
Integrated care
What is integrated care? Integrated care refers to the association of multiple treatment paradigms to produce a single unified program. The idea is to deliver seamless care to the patient to ensure high treatment continuity and improve patient satisfaction. Integrated programs typically involve multi-element psychosocial therapies for mental illness. For example, integrated psychological therapy and integrated neurocognitive therapy involves a combination of cognitive and social skills training. Integrated care can also refer to the formal liaison of typically distinct services such as medical practitioners and dedicated mental health teams, or the incorporation of mental health and substance use treatments into…

Life skills programs
What are life skills programs? Life skills programs are designed to allow people with severe mental disorders such as schizophrenia to achieve greater independence, social and community functioning. For example, a life skills program may involve training in money management, organising and running a home, domestic skills, hygiene and personal care, and interpersonal skills. These programs can be organised through a day-centre unit, attended by residents of either hospitals or the community, on an individual basis or in a group setting. What is the evidence for life skills programs? Moderate to low quality evidence suggests life skills programs are beneficial…
Metacognitive training
What is metacognitive training? Research has found that many people with schizophrenia have biased cognitive processes, and have a lack of insight about these problems. Biased cognitive processes are thought to underlie delusional beliefs. The aim of metacognitive training is to make patients aware of delusion-relevant cognitive biases and then to amend these biases. Cognitive biases in people with schizophrenia involve a tendency to jump to conclusions based on a small amount of information, and make errors when trying to find reasons for their own and others’ behaviours. Research has shown that people with schizophrenia are often unsure about their…

Mindfulness
What are mindfulness and acceptance therapies? Mindfulness and acceptance therapies involve intentional and non-judgmental focus of one’s attention on emotions, thoughts and sensations that are occurring in the present moment. The aim is to open awareness to present experiences, whether positive or negative, allowing thoughts and voices to come and go without reacting, and accepting oneself and the experience. This may help alleviate the distress associated with symptoms by focusing on how people relate and respond to their psychotic experiences, rather than identifying and directly challenging thoughts and beliefs about these experiences. What is the evidence for mindfulness and acceptance…

Monetary incentives
What are monetary incentives? Monetary incentives have been proposed as a form of positive behavioural reinforcement, given as a reward for the implementation of target behaviour. In the real world this can include employment or living allowances, but they can be items of lower value that have greater symbolic significance. At the lowest end these incentives become valueless tokens (see the token economies topic). What is the evidence for monetary incentives? Moderate to low quality evidence finds contingency reinforcement with monetary rewards in combination with nicotine replacement therapy is more effective than contingency reinforcement alone or self-quit for reducing smoking….

Morita therapy
What is Morita Therapy? Morita therapy is a treatment approach developed by Shoma Morita and is most commonly used in some Asian countries, including Japan and China. Morita therapy focuses on mental health from a collective perspective, rather than the perspective of the individual, removing the preoccupation with symptoms and instead focusing on constructive behaviours. While some Morita therapy programs have been updated and shortened (~4 weeks), the original Morita therapy guideline is divided into four phases: a) 7 days of isolated bed rest, with no access to any form of entertainment, b) 4 to 7 days of light work…

Music therapy
What is music therapy? Music therapy utilises musical experiences and interactions designed to assist people with disorders such as schizophrenia to address issues they may have difficulty with, such as communication and self-regulation. It may be offered through group and individual programmes and does not require a client to have musical skills. Therapists are trained to respond to challenging behaviour using both musical and non-musical strategies. Music therapy can be active (including improvisation, producing music) or receptive (listening to either live or recorded music). The musical therapist can manipulate the rhythmic or harmonic structure to alter therapy intensity. The therapist…

Nidotherapy
What is nidotherapy? Nidotherapy is a psychological therapy that aims to identify and alleviate problematic areas affecting a person’s life and surroundings. While typical psychological therapies aim to create changes within a person’s actions, emotions, or thoughts, nidotherapy instead aims to make changes to a person’s environment and life situation, with the goal of enabling improvements in quality of life, relationships, mental health and self-esteem. What is the evidence for nidotherapy? Low quality evidence is unable to determine the effectiveness of nidotherapy for social functioning or mental health. Review authors conclude that until further research is conducted, nidotherapy should be…

Open dialogue approach
We have not found any systematic reviews on this topic that meet the Schizophrenia Library’s inclusion criteria. Pending enough primary studies, we invite reviews on this topic to be conducted. Alternatively, we will endeavour to conduct our own review to fill this gap in the Library. September 2020

Peer support
What is peer support? Peer support involves providing support or services to people with mental health problems by other people who have experienced mental health problems. Peer support may promote confidence and hope through sharing experiences and modelling recovery and coping strategies. The potential for recipients of peer support to provide reciprocal support may also be empowering and of therapeutic value. What is the evidence for peer support? With unidirectional peer support, moderate to low quality evidence suggests a small effect of improved recovery and hope at the end of treatment and at follow-up, and improved depression and anxiety, quality…

Physical restraint
What is physical restraint? The management of acutely disturbed patients poses a challenge for mental health services. Some patients may be suicidal while others may pose a danger to staff or other patients. The challenge is to maintain the safety of all patients and staff, while providing a therapeutic environment. Management techniques for dealing with patients who become excessively agitated, aggressive, or violent may include the use of physical restraint, seclusion or containment. What is the evidence for physical restraint ? Moderate to low quality evidence suggests prevalence rates of restraint vary across countries, from 3.8% of patient admissions in…

Prevention programs
We have not found any systematic reviews on this topic that meet our inclusion criteria. Pending enough primary studies, we invite reviews on this topic to be conducted. Alternatively, we will endeavour to conduct our own review to fill this gap in the Library. September 2020

Problem solving skills training
What is problem solving skills training? People with severe mental illnesses such as schizophrenia may show impairments in problem-solving ability. Training interventions can help develop problem solving skills, by teaching people strategies for tackling a particular problem, and ideally, teaches skills that can be reapplied in the future. A typical problem-solving therapy approach includes several key stages; linking symptoms to problems, defining the problem, setting achievable goals, generating solutions, and evaluating results. What is the evidence for problem solving skills training? Low quality evidence is unable to determine any benefit of problem solving skills training over routine care, coping skills…

Psychodynamic psychotherapy
What is psychodynamic psychotherapy? Psychodynamic psychotherapy and psychoanalysis are types of individual psychotherapy which attempt to explore the influence of a person’s previous emotional experiences on their current mental state, particularly in the context of the ‘transference’ of feelings from one focus to another. The methods employ free association, recall and interpretation of dreams, and exploration of ‘resistance’ to recovery. This is a controversial approach that has gained more support since the inclusion of other elements, such as supportive and directive techniques. However, they are usually only used in the treatment of schizophrenia when they are integrated into a multi-modal…

Shared decision making
What is shared decision making? Shared decision making aims to support patients during specialist mental health treatment, encouraging patients to be active in the decision making process for their pharmacological and psychoeducational treatment options, by keeping them informed and involved. Shared decision making interventions often utilise a decision-making tool, involving the patient in the decision making process in conjunction with nursing support, ensuring that they understand the clinical problem, exploring patients’ worries, fears and expectations, discussing potential treatment options and ensuring the implications of these options are understood, and providing opportunities to review decisions. What is the evidence for shared…

Strengths-based delivery
What is strengths-based delivery? The strengths-based delivery approach is a person-centred approach that supports commitment to individual development and growth. The approach favours a low case manager load, low supervisor to case manager ratio, and structured weekly group supervision to ensure adherence to the principles of the model. Strengths assessment and personal recovery plans are developed in collaboration between service users and practitioners. Interventions are tailored to meet individual needs, with an emphasis on existing resources, such as supported employment, supported housing, supported education, and supported recreation. What is the evidence for strengths-based delivery? Low quality evidence is unable to…

Supported housing
What is supported housing? Support housing services may include group homes, hostels, therapeutic communities, or supported independent tenancies, and incorporate availability of outreach care workers who visit or who are located on-site. These programs are designed to support people with severe mental disorders such as schizophrenia living in the community, who are not living with family or in residential care, in order to increase independence, quality of life, and achieve greater social and community functioning. What is the evidence for supported housing programs? Low quality evidence is unclear as to the benefit of supported housing for improving outcomes for people…

Supportive therapy
What is supportive therapy? Therapeutic support is a key component of the successful treatment of schizophrenia, most providing the opportunity to listen to patients’ concerns, give encouragement, and arrange assistance for practical problems. A definition of ‘supportive therapy’ can include a variety of interventions, ranging from traditional supportive psychotherapy with a clinician, to mental health workers providing practical support. This type of therapy aims to support people with schizophrenia living in the community or in treatment facilities to increase self-esteem, quality of life, and achieve greater social and community functioning. What is the evidence for supportive therapy? Moderate to low…

Telemental health
What is telemental health? There is a growing need to deliver low-cost treatments tailored to individual needs and delivered in a continuous way (e.g. all year long) from any location. Telemental health (or “ehealth”) has the potential to meet this need. Telemental health refers to any mental health treatment that is provided electronically, either by telephone or internet such as online health programs, or video conferencing. This type of intervention involves structured counselling and generally aims to increase medication adherence and prevent relapse. Importantly, it also removes geographic barriers to care. What is the evidence for telemental interventions? Moderate to…

Therapeutic relationship
What are therapeutic relationships? The therapeutic relationship refers to the relationship between a patient and a clinician. Many patients consider it to be the most important component of care, and therefore it should influence how well patients engage with services, and how well they show improvements from therapy. What is the evidence for therapeutic relationships? Low quality evidence is unable to determine any associations between therapeutic relationships and hospitalisation rates, symptoms or functioning. Review authors conclude that there is some, but not overwhelming evidence that good therapeutic relationships predict good outcomes, but that methodologically rigorous research is required to properly…

Token economies
What is a token economy? A token economy is a behavioural therapy utilising non-monetary ‘tokens’ as a reward to reinforce target behaviours. These tokens have no intrinsic value but can be exchanged for various goods or privileges. Token economies were used widely for schizophrenia in the 1960’s and 1970’s, targeted specifically at negative symptoms such as poor motivation or attention, and social withdrawal. More recently token therapies have largely been replaced by social and life skills training, and cognitive skills training. What is the evidence for token economies? Moderate to low quality evidence finds no benefit of token economies for…

Trauma-focused therapies
What are trauma-focused therapies? Trauma-focused therapies involve identifying and processing traumatic memories, changing unhelpful beliefs about these memories, and developing new ways of responding to associated triggers. Exposure to traumatic or adverse experiences represents a risk factor in the development of schizophrenia. Given the potential overlap between trauma and psychotic symptoms, trauma-focused therapies may be effective adjunctive treatments for people with schizophrenia. What is the evidence for trauma-focused therapies? Moderate to low quality evidence suggests trauma-focused therapies may improve positive symptoms immediately post-treatment, and may have longer-term effects on delusions and trauma symptoms. Exposure-based therapies (prolonged exposure, written exposure, elements…

User-held records
What are user-held records? User-held information is where the patient holds information about their care. Providing people with information about their care increases feelings of involvement in treatment, and should increase satisfaction and participation with services, ensure early treatment and prevent hospital admission. Some research suggests that while many people decline the offer of a user-held record, the majority of those who carry their records report this to be useful. What is the evidence for user-held records? Moderate to high quality evidence finds no benefit of user-held records over standard care for a reduction in hospital readmissions. September 2020

Virtual reality and avatar therapy
What is virtual reality and avatar therapy? Virtual reality is a modern computerised real-time technology using graphics, sounds and other sensory input, which creates an interactive computer-mediated world. Virtual reality applications have been primarily used for the assessment and treatment of anxieties and phobias. More recently they have been used to examine the perception of emotion and the emotional responses of people with schizophrenia during simulated social encounters, with the aim of improving social skills, cognitive functioning, and treatment adherence. Avatar therapy uses virtual reality to recreate the faces and voices of hallucinations. Using a computer program, patients create an…
Green - Topic summary is available.
Orange - Topic summary is being compiled.
Red - Topic summary has no current systematic review available.
